Relating the rate of growth of metal nanoparticles to cluster size distribution in electroless deposition†
Abstract
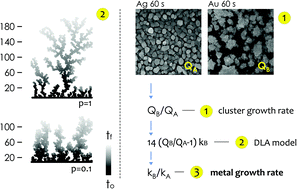
Electroless deposition on patterned silicon substrates enables the formation of metal nanomaterials with tight control over their size and shape. In the technique, metal ions are transported by diffusion from a solution to the active sites of an autocatalytic substrate where they are reduced as metals upon contact. Here, using diffusion limited aggregation models and numerical simulations, we derived relationships that correlate the cluster size distribution to the total mass of deposited particles. We found that the ratio ξ between the rates of growth of two different metals 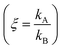 depends on the ratio γ between the rates of growth of clusters formed by those metals
depends on the ratio γ between the rates of growth of clusters formed by those metals 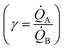 through the linearity law ξ = 14(γ − 1). We then validated the model using experiments. Different from other methods, the model derives k using as input the geometry of metal nanoparticle clusters, decoded by SEM or AFM images of samples, and a known reference.
through the linearity law ξ = 14(γ − 1). We then validated the model using experiments. Different from other methods, the model derives k using as input the geometry of metal nanoparticle clusters, decoded by SEM or AFM images of samples, and a known reference.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...