Functionalized branched polymers: promising immunomodulatory tools for the treatment of cancer and immune disorders
Abstract
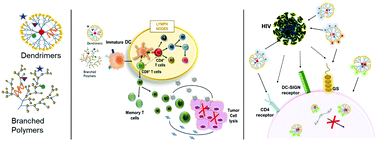
Well-defined synthetic branched nanostructures form an emerging subclass of macromolecular structures whose 3D structure and multivalency offer unique opportunities for fine-tuning internalization and cellular targeting. Dendrimers possess a well-defined 3D-globular backbone with highly versatile functional surface groups and exhibit a range of chemical and biological properties. Branched polymers present unique opportunities for the targeted delivery of diverse bioactive molecules (including targeting ligands, imaging probes, and drugs) via conjugation to multiple sites within the structure. The inherent versatility and multifunctionality of these architectures make them potentially useful for the modulation of multiple immune-related pathways for the treatment of a wide range of diseases and disorders, including cancer and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Herein, we describe the key components of the immune system whose targeting can help overcome immune-related disorders and discuss branched polymers (including dendrimers) as promising delivery systems with unique immunomodulatory properties against cancer and infectious diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...