Effects of chain length on the size, stability, and electronic structure of redox-active organic–inorganic hybrid polyoxometalate micelles†
Abstract
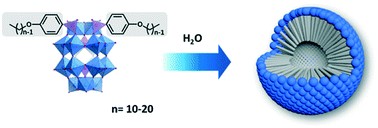
Double-chain redox-active surfactants based on hybrid polyoxometalates show solvent-dependent assembly into nanoscale micellar architectures. These organic–inorganic hybrid amphiphiles, of the general formula K6[P2W17O61(POC6H4O(CnH2n+1))2], were prepared with varying aliphatic chain lengths (n = 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 and 20) and display different multi-electron redox behaviours in their molecular and supramolecular forms. Furthermore, modification of the length of the hydrophobic tail is an effective strategy for controlling the stability and electronic properties of the supramolecular nanostructures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...