Small antibacterial molecules highly active against drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus†
Abstract
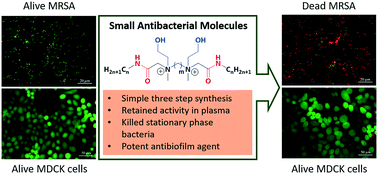
The rapid growth of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus coupled with their biofilm forming ability has made the infections difficult to treat with conventional antibiotics. This has created a massive threat towards public health and is a huge concern worldwide. Aiming to address this challenging issue, herein we report a new class of small antibacterial molecules (SAMs) with high antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant S. aureus. The design principle of the molecules was based on the variation of hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance through incorporation of two quaternary ammonium groups, ethanol moieties, non-peptidic amide bonds and aliphatic chains. The lead compound, identified through a comprehensive analysis of structure–activity relationships, displayed high activity against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA) with MIC values in the range of 1–4 μg mL−1. More importantly, this compound was capable of killing stationary phase bacteria and disrupting established biofilms of MRSA. Additionally, the compound revealed minimum toxicity towards human erythrocytes (HC50 = 577 μg mL−1) and did not show significant toxicity towards mammalian cells (MDCK and A549) up to 128 μg mL−1. Remarkably, the incorporation of non-peptidic amide bonds made the compounds less susceptible to degradation in human plasma, serum and mouse liver homogenate. Taken together, the results therefore indicate great promise for this class of molecules to be developed as potent antibacterial agents in treating infections caused by drug-resistant S. aureus.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Antimicrobial Resistance


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...