How mithramycin stereochemistry dictates its structure and DNA binding function†
Abstract
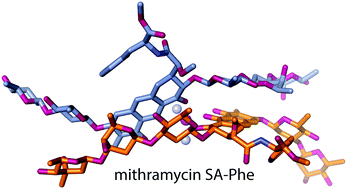
An aureolic acid natural product mithramycin (MTM) has been known for its potent antineoplastic properties. MTM inhibits cell growth by binding in the minor groove of double-stranded DNA as a dimer, in which the two molecules of MTM are coordinated to each other through a divalent metal ion. A crystal structure of an MTM analogue, MTM SA-Phe, in the active metal ion-coordinated dimeric form demonstrates how the stereochemical features of MTM define the helicity of the dimeric scaffold for its binding to a right-handed DNA double helix. We also show crystallographically and biochemically that MTM, but not MTM SA-Phe, can be inactivated by boric acid through formation of a large macrocyclic species, in which two molecules of MTM are crosslinked to each other through 3-side chain–boron–sugar intermolecular bonds. We discuss these structural and biochemical properties in the context of MTM biosynthesis and the design of MTM analogues as anticancer therapeutics.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Natural Products


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...