Preparation and evaluation of 99mTc-labeled porphyrin complexes prepared using PNP and HYNIC cores: studying the effects of core selection on pharmacokinetics and tumor uptake in a mouse model†
Abstract
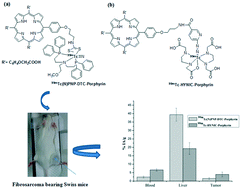
Porphyrins are tetrapyrrolic macrocyclic ligands known for their affinity towards neoplastic tissues and once radiolabeled with a suitable diagnostic radioisotope could potentially be used for the imaging of tumorous lesions. In the present study, an unsymmetrically substituted porphyrin derivative namely 5-(p-amino-propyloxyphenyl)-10,15,20-tris(carboxymethyleneoxyphenyl)-porphyrin was synthesized and modified further to enable radiolabeling with 99mTc using two different 99mTc-cores viz.99mTc-HYNIC (hydrazino nicotinic acid) and 99mTc(N)PNP2 (PNP2 = bis-[(2-dimethylphosphino)ethyl]-methoxy-ethylamine) in order to study the effect of employing different 99mTc-cores on tumor affinity and pharmacokinetic behavior of the resultant 99mTc-labeled porphyrin complexes. 99mTc–Porphyrin complexes were characterized by reversed phase HPLC studies and could be prepared with >95% radiochemical purity under optimized radiolabeling conditions. Both 99mTc-complexes were found to be adequately stable in human blood serum till 3 h post-preparation. Bio-distribution studies, carried out in Swiss mice bearing fibrosarcoma tumors, revealed relatively higher tumor uptake for the 99mTc-HYNIC–porphyrin complex (3.95 ± 1.42 and 3.28 ± 0.27% IA per g) compared to that exhibited by the 99mTc(N)PNP-DTC–porphyrin complex (1.52 ± 0.53 and 1.56 ± 0.10% IA per g) at 1.5 and 3 h post-administration, although the former complex exhibited comparatively lower lipophilicity in the octanol–water system. Higher uptake and longer retention in the blood were observed for the 99mTc-HYNIC–porphyrin complex (6.63 ± 0.75 and 4.36 ± 0.25% IA per g) compared to that exhibited by the 99mTc(N)PNP-DTC–porphyrin complex (2.41 ± 0.54 and 2.30 ± 0.16% IA per g) at both 1.5 and 3 h post-administration. However, relatively lower liver uptake was observed for the former complex (19.26 ± 3.48 and 18.45 ± 1.05% IA per g) than that exhibited by the latter one (39.37 ± 3.88 and 34.15 ± 8.25% IA per g) at both 1.5 and 3 h post-administration. This study indicates that the in vivo behavior exhibited by the 99mTc-labeled porphyrins not only depends on their lipophilicity/hydrophilicity but is also governed by the Tc-cores employed for radiolabeling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...