Benzoflavone derivatives as potent antihyperuricemic agents†
Abstract
Two series of benzoflavone derivatives were rationally designed, synthesized and evaluated for their xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory potential. Among both series, eight compounds (NF-2, NF-4, NF-9, NF-12, NF-16, NF-25, NF-28, and NF-32) were found to exert significant XO inhibition with IC50 values lower than 10 μM. Enzyme kinetic studies revealed that the most potent benzoflavone derivatives (NF-4 and NF-28) are mixed type inhibitors of the XO enzyme. Molecular modeling studies were also performed to investigate the binding interactions of these molecules (NF-4 and NF-28) with the amino acid residues present in the active site of the enzyme. Docking results confirmed that their favorable binding conformations in the active site of XO can completely block the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Benzoflavone derivatives exhibiting potent XO enzyme inhibition also showed promising results in a hyperuricemic mice model when tested in vivo.
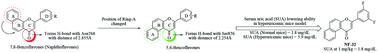


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...