Shift of ionization equilibrium in spatially confined laser induced plasma
Abstract
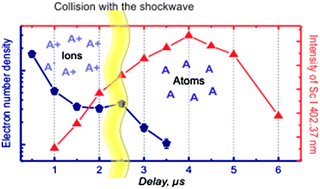
Spatial confinement of laser-induced plasmas has been recognized in the last decade as one of the ways to enhance the sensitivity of trace detection. However, there is no clear explanation for the fact that some lines are enhanced while others, in contrast, are weakened in confined plasma. In this work, we investigated the causes of the opposite changes of atomic and ionic lines in spatially confined plasma. For this purpose, we designed two cylindrical microchambers (2 and 4 mm in diameter) with side-on collection of emission. Plasma evolution in these chambers was studied at two laser energies: 70 mJ and 240 mJ. An accurate estimate of plasma parameters demonstrated that there were no changes in the low energy regime, while sharp changes both in T and especially Ne were observed for the two microchambers in the high energy regime. The features of evolution curves, such as the maximum and its temporal position, are explained by a shift of ionization equilibrium towards neutral atoms in the plasma after compression by the reflected shock wave. This clearly explains the differences in the evolution of the intensities of atomic and ionic lines: Al II 281.62 nm and Mg II lines are decreased rapidly, while atomic lines Sc I 402.37 nm and Mg I 277.98 nm are strongly enhanced at delays of 3–4 μs. Another observation is mixing of the plume and the consequent reduction of self-absorption for resonance lines due to collision of the shock wave with the plasma front.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...