A quantitative nanoparticle extraction method for microsecond time resolved single-particle ICP-MS data in the presence of a high background†‡
Abstract
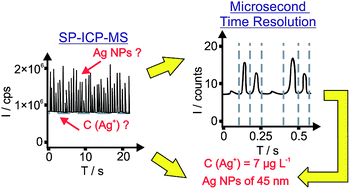
The detection of nanoparticles (NPs) in the presence of a high background (BG) is challenging in single particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SP-ICP-MS) and leads to inaccurate quantification. In this study, we report a data processing procedure for the deconvolution of SP-ICP-MS data and its application to quantification of both the Ag NP size distribution (20 to 100 nm Ag NPs) and the concentration of dissolved silver ions (Ag+ up to 7.5 μg L−1) in mixtures using Poisson statistics to determine thresholds to identify the beginning and end of NP signal events. SP-ICP-MS with a microsecond time resolution data acquisition system (μsDAQ) and conventional pneumatic nebulization was used for the detection of Ag NPs in the presence of a significant concentration of ionic BG (107Ag+ up to 1 000 000 cps). In contrast to conventional three times standard deviation of the BG (3 × SDBG) decision criterion (normal distribution), our NP ion cloud extraction mechanism from the μsDAQ is based on setting thresholds to determine the beginning and the end of an ion cloud using Poisson statistics, which is suitable for the low count data. The algorithm was applied here for the flagging and detection of Ag NPs in the presence of Ag+. Critical level (false positive probability was set to 5%) and detection limit (false positive and false negative probabilities were set to 5%) based on Poisson distributions were implemented to determine the thresholds. A range of different sets of NP ion cloud extraction conditions were tested to verify the calculated thresholds and to obtain optimal extraction conditions at different BGs (Ag+ concentration). The method can be universally applied for the detection of different elements with SP-ICP-MS.
- This article is part of the themed collections: JAAS Recent Open Access Articles and Community Leaders: Alfredo Sanz-Medel


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...