Production of 3-hydroxypropionate using a novel malonyl-CoA-mediated biosynthetic pathway in genetically engineered E. coli strain†
Abstract
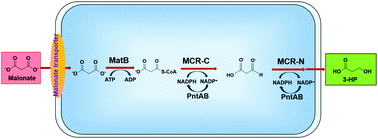
3-Hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) is a promising platform chemical with a wide range of applications. The traditional chemical synthesis of 3-HP is well-established, but the resource limitations, high price and toxicity of the used raw materials do not meet the new sustainable development goals. Accordingly, the microbial synthesis of 3-HP by fermentation will become a promising and attractive route mainly due to its environmentally friendly production, use of renewable resources, and sustainable development. Herein, to biosynthesize 3-HP directly from malonate, a novel malonyl-CoA-mediated biosynthetic pathway was successfully developed as follows. Firstly, various transporters involved in malonate transportation was systematically investigated and screened. Secondly, to biosynthesize 3-HP, an original strategy was employed by heterologously co-expressing the mutant of malonyl-CoA reductase (MCR) from Chloroflexus aurantiacus and malonyl-CoA synthetase (MatB) from Rhodopseudomonas palustris in the Escherichia coli C43 (DE3) strain, which was screened from three different MatB enzymes. Finally, to further enhance the production of 3-HP, native transhydrogenase (PntAB) and NAD kinase (YfjB) genes were expressed to increase the NADPH supply in E. coli. The final genetically modified strain SGN78 showed a significant improvement in malonate utilization and produced 1.20 ± 0.08 g L−1 of 3-HP in the flask culture. Thus, this work demonstrates the production of 3-HP in E. coli with the shortest route for the biosynthesis of 3-HP, which involved only three steps from the substrate. Also, it opens a path for the biosynthesis of 3-HP and other malonyl-CoA-based valuable chemicals directly from malonate in E. coli.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...