A sustainable biochar catalyst synergized with copper heteroatoms and CO2 for singlet oxygenation and electron transfer routes†
Abstract
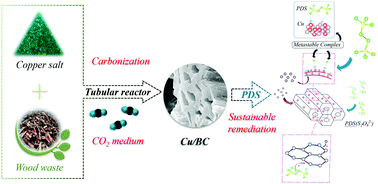
We have developed a wood waste-derived biochar as a sustainable graphitic carbon catalyst for environmental remediation through catalytic pyrolysis under the synergistic effects between Cu heteroatoms and CO2, which for the first time are found to significantly enhance the oxygen functionalities, defective sites, and highly ordered sp2-hybridized carbon matrix. The copper-doped graphitic biochars (Cu-GBCs) were further characterized by XRD, FTIR, Raman, XPS, etc., revealing that the modified specific surface area, pore structure, graphitization, and active sites (i.e., defective sites and ketonic group) on the Cu-GBCs corresponded to the synergistic Cu species loading and Cu-induced carbon-matrix reformation in CO2 environment during pyrolysis. The catalytic ability of Cu-GBCs was evaluated using the ubiquitous peroxydisulfate (PDS) activation system for the removal of various organic contaminants (i.e., rhodamine B, phenol, bisphenol A, and 4-chlorophenol), and gave the highest degradation rate of 0.0312 min−1 in comparison with those of pristine GBCs and N2-pyrolyzed Cu-GBCs ranging from 0.0056 to 0.0094 min−1. The synergistic effects were attributed to the encapsulated Cu heteroatoms, evolved ketonic groups, and abundant unconfined π electrons within the carbon lattice. According to scavenger experiments, ESR analysis, and two-chamber experiments, selective and sustainable non-radical pathways (i.e., singlet oxygenation and electron transfer) mediated by the Cu-induced metastable surface complex were achieved in the Cu-GBC/PDS system. This study offers the first insights into the efficacy, sustainability, and mechanistic roles of Cu-GBCs as an emerging carbon-based catalyst for green environmental remediation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...