Towards sustainable elastomers from CO2: life cycle assessment of carbon capture and utilization for rubbers†
Abstract
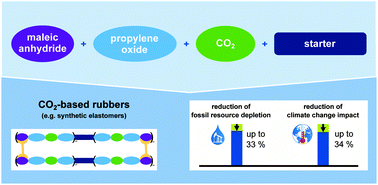
Elastomers have been recently proposed to integrate CO2 as carbon feedstock. These elastomers are produced by reacting carbon dioxide with propylene oxide and maleic anhydride. The resulting cross-linkable polyether carbonate polyols can be combined with isocyanates to form a novel class of polymers: CO2-based rubbers. These CO2-based rubbers are able to substitute conventional rubbers in synthetic elastomer products, such as sealants or flexible tubes. In this work, we present the first Life Cycle Assessment for CO2-based rubbers. To compare CO2-based and conventional rubbers our assessment considers all relevant life cycle stages from cradle-to-grave. The production system of CO2-based rubbers encompasses a nearby ammonia plant as a CO2 source, the conversion of CO2 to polyols, the reaction of polyols with isocyanates and finally, the incineration of CO2-based rubbers. Our analysis shows that CO2-based rubbers containing approx. 20% wt. CO2 have a global warming impact of 4.93 kg CO2-eq. Thus, CO2-based rubbers are no carbon sink. However, CO2-based rubbers reduce global warming impact by up to 34% if they substitute, for example, hydrogenated nitrile butadiene rubber on an equal mass basis. Fossil resource depletion is reduced by up to 33%. In contrast, other impact categories like ionizing radiation are increased by the utilization of CO2-based rubbers in some cases. Thus, our study indicates that CO2-based rubbers provide a promising pathway to reduce global warming impact and fossil resource depletion. However, it is likely that some other environmental impact categories such as ionizing radiation and freshwater eutrophication are increased.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...