Highly-efficient and magnetically-separable ZnO/Co@N-CNTs catalyst for hydrodeoxygenation of lignin and its derived species under mild conditions†
Abstract
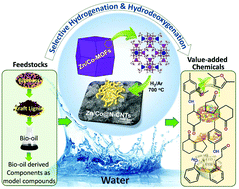
A catalyst comprising highly-efficient and magnetically-separable bimetallic ZnO and Co nanoparticles (NPs) deposited on N-doped carbon nanotubes (ZnO/Co@N-CNTs) was synthesized by the direct calcination of the bimetallic Zn/Co zeolitic imidazolate framework (Zn/Co-ZIF) for the effective hydrogenation (HD) and hydrodeoxygenation (HD) of lignin and its derived species. During the calcination of Zn/Co-ZIF, Zn was dislocated from the framework to the particle surface to form amorphous ZnO NPs and metallic Co NPs, which activated the growth of the N-CNTs. Because of the highly Lewis acidic amorphous ZnO, high HD/HDO ability of metallic Co NPs, and high wettability of the N-CNT, an almost complete conversion of vanillin into its corresponding deoxygenated species, creosol, was achieved in an aqueous medium without the production of byproducts under mild reaction conditions (150 °C, 0.7 MPa H2, a reaction time of 2 h). When kraft lignin and bio-oil derived from concentrated strong acid hydrolysis lignin were converted over ZnO/Co@N-CNTs, high degrees of deoxygenation of 74.2% and 34.4%, respectively, could be achieved at 350 °C, 5.0 MPa H2, and a reaction time of 6 h in water. A detailed chemical composition analysis of the deoxygenated bio-oil revealed that cyclohexanone and its alkyl group-substituted derivatives were the major species. To gain insight into the HD/HDO mechanisms, various types of lignin-derived monomers (syringaldehyde, acetovanillone, acetosyringone, 2-phenoxy-1-phenylethanol, cinnamaldehyde, isoeugenol) and holocellulose-derived monomers (furfural and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural), different types of catalysts, and various reaction parameters were tested. The mild reaction conditions, use of a non-noble metal catalyst, and use of water as the solvent make it possible to develop a cost-effective, easy to scale up, and environmental-benign process for biofuel and biochemical production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...