Design of high-performance heterogeneous catalysts using hydrotalcite for selective organic transformations†
Abstract
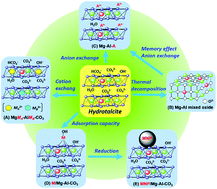
Hydrotalcite (HT) is an anionic layered double hydroxide clay, consisting of positively charged Brucite-like layers. To compensate for the positive charges, various inorganic and organic anions are located within the interlayer along with water. Hydrotalcite exhibits the characteristic cation-exchange features of the Brucite-like layer, the anion exchangeability of the interlayer, a memory effect, and tunable basicity and adsorption capacity. Based on these features, nanostructured metal species on HTs were prepared in a much simpler way than those previously reported; this provides a strong protocol for the preparation of catalytically active species with uniform composition that are evenly distributed on the solid surface. This review focuses on the design of high-performance heterogeneous catalysts using HT and HT-like compounds for selective molecular transformations under liquid-phase conditions. Catalytic systems that use HT offer significant benefits for achieving green organic syntheses because of the following: (i) they use nonpolluting reagents, (ii) they exhibit high catalytic activities and selectivities, (iii) they tolerate a wide range of substrates, and (iv) a simple work-up procedure facilitates easy catalyst recovery and reuse. Furthermore, highly atom-economical catalytic reactions, such as multiple reactions in a single pot, can be realized by using the novel HT-based catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...