Development of a waste-derived lignin-porphyrin bio-polymer with enhanced photoluminescence at high water fraction with wide pH range and heavy metal sensitivity investigations†
Abstract
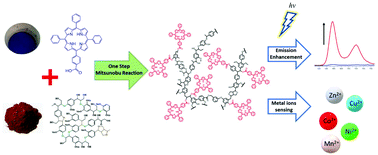
Lignin is a common by-product of pulping industries. Diverse functional groups in the polymeric matrix make lignin a superior alternative for carbon-based materials. Meanwhile, porphyrin family is well known in multiple applications; however, aggregation-caused quenching (AQC) due to the strong π–π interaction in poor-solvent environments will limit the photoluminescence intensity of porphyrin. In this study, a new lignin-porphyrin (AL–CTPP) polymer was developed, which combined and promoted the functionalities of the two chemicals. In photoluminescence investigations, the emission intensity of AL–CTPP in the 600 to 780 nm region was 30-fold stronger than that of porphyrin alone when the water fraction (fw) > 0.9. Lignin served as a stable backbone immobilizing porphyrin and prevented unwanted aggregation of porphyrin and the related aggregation-caused quenching in high fw solution at various pH. Furthermore, linear correlations were established between absorption properties of AL–CTPP with concentrations of five metal ions (i.e., Mn2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+). With these unique features, AL–CTPP showed enhanced performance for potential bio-imaging and environmental applications. Lignin-porphyrin polymers may represent a significant potential product of biorefineries and the effective utilization of lignin to fabricate a new functional material which offers significant benefits to support waste valorization.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Green Biorefinery Technologies based on Waste Biomass


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...