Black soybean seed coat polyphenols promote nitric oxide production in the aorta through glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from the intestinal cells
Abstract
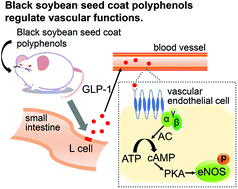
Black soybean seed coat polyphenols were reported to possess various bioregulatory functions. However, the effects of black soybean seed coat polyphenols on vascular functions are unknown. Vascular dysfunction caused by aging and vascular stiffness is associated with a risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), and a reduction in nitric oxide (NO) levels can trigger the onset of CVD. In the present study, we investigated the effect of polyphenol-rich black soybean seed coat extract (BE) on vascular functions and the underlying mechanisms involved. The oral administration of BE at 50 mg per kg body weight to Wistar rats increased NO levels as determined by eNOS phosphorylation. The administration of BE also increased GLP-1 and cAMP levels. Furthermore, the effects of BE were inhibited in the presence of a GLP-1 receptor antagonist. This suggests that GLP-1 is strongly involved in the underlying mechanism of NO production in vivo. In conclusion, BE contributes to the improvement of vascular functions by promoting NO production. Regarding the putative underlying mechanism, GLP-1 secreted from intestinal cells by the polyphenols in BE activates eNOS in vascular endothelial cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...