9t18:1 and 11t18:1 activate the MAPK pathway to regulate the expression of PLA2 and cause inflammation in HUVECs
Abstract
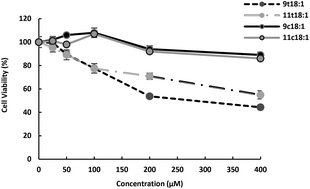
trans fatty acids (TFAs) have been reported to promote vascular diseases mainly by promoting apoptosis and inflammation of vascular endothelial cells. However, it has been reported in recent years that elaidic acid (9t18:1) and vaccenic acid (11t18:1) may have different effects on vascular health. This study investigated the effects of 9t18:1 and 11t18:1 on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) function and the possible mechanism of inflammation by analyzing the changes in the phospholipid composition and the relationship between phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and MAPK pathway. Here we found that the effect of 11t18:1 on cell viability, membrane damage and cellular inflammation was significantly lower than that of 9t18:1 (p < 0.05). And 9t18:1 and 11t18:1 had different effects on phospholipid composition. Both 9t18:1 and 11t18:1 significantly increased the protein expression of PLA2. Moreover, the MAPK pathway regulated the expression of PLA2, inflammatory cytokines and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and the secretion of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in HUVECs induced by 9t18:1 and 11t18:1. In conclusion, 9t18:1 and 11t18:1 activated the MAPK pathway which regulated the expression of PLA2 to cause inflammation in HUVECs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...