Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch polysaccharide prevents hepatic steatosis in high fructose-fed mice associated with changes in the gut microbiota
Abstract
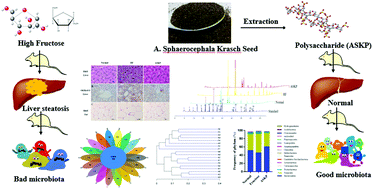
High fructose (HF) diet-induced liver steatosis is associated with intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. The aim of this study was to assess the modulatory effects of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krash seed polysaccharide (ASKP) on fatty acid metabolism and intestinal microbiota in mice fed with HF water. Administration of HF-fed mice with ASKP prevented fat accumulation and blunted metabolic inflammation and endotoxaemia. ASKP-treated mice displayed improved glucose tolerance and fully exhibited protection against hepatic steatosis. Besides, ASKP was effective in improving the changes in the composition of liver fatty acids via modulating hepatic SREBP-1c, SCD-1, ACC and FAS expressions. 16S rRNA gene sequencing showed that ASKP treatment modified the gut microbial species at the phylum level with a decrease of Firmicutes and a slight increase of Bacteroidetes (p > 0.05). Interestingly, ASKP markedly increased the proportion of the mucin-degrading bacterium Akkermansia at the genus level in HF-fed mice. These findings support the beneficial metabolic effects of ASKP through amelioration of the HF-induced features of liver steatosis, which is associated with health maintenance of the intestinal microecosystem.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...