Trametes orientalis polysaccharide alleviates PM2.5-induced lung injury in mice through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities
Abstract
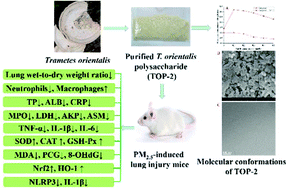
This paper examined the molecular conformation of Trametes orientalis polysaccharide (TOP-2) and evaluated the ameliorative effects of TOP-2 on PM2.5-induced lung injury in mice. The Congo red test and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed that TOP-2 had a triple-helical structure. PM2.5-induced pulmonary edema was ameliorated by TOP-2 intervention. PM2.5 notably increased the number of inflammatory cells and percentages of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and notably reduced the percentages of macrophages in BALF, while TOP-2 abolished these effects. The increased levels of total protein, albumin, C-reactive protein (CRP), myeloperoxidase (MPO), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), acid sphingomyelinase (ASM), TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in BALF after PM2.5 exposure were inhibited by TOP-2. In addition, TOP-2 could not only remarkably promote the activities of antioxidant enzymes, but also reduce the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), protein carbonyl group (PCG) and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG). Furthermore, TOP-2 up-regulated the expressions of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and inhibited the activation of NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in the lung tissue. These results hint that TOP-2 could alleviate PM2.5-induced lung injury in mice via its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, and the underlying mechanisms, at least partly, depended on activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...