Phenolic content and potential bioactivity of apple juice as affected by thermal and ultrasound pasteurization
Abstract
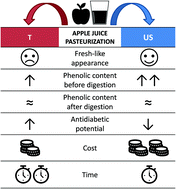
Thermal (T) and ultrasound (US) pasteurization processes were applied to apple juice and the phenolic compounds (TPC) were quantified before and after in vitro digestion by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn, with their bioaccessibility ascertained. Digested samples were analysed for their inhibitory capacity against α-glucosidase. Since some of the compounds exhibit fluorescence, both steady state and time-resolved fluorescence methods were used to investigate the binding to a blood transport protein, human serum albumin (HSA). It was found that processing induced an increase in the TPC content, which was more pronounced when US was applied. In contrast, digestion reduced the TPC content, evening out the overall effect. Still T and US pasteurized juices exhibited a higher quantity of TPC upon digestion as compared to the raw sample. No correlation was found between the TPC content and α-glucosidase inhibition, as the T and US pasteurized juices showed the highest and lowest inhibitory capacities against the enzyme, respectively. This is indicative that other compounds, such as those formed upon thermal treatment, may be involved in the antidiabetic effect of apple juice. The fluorescence study showed that binding occurred to HSA, at slightly different rates for different species present in the US treated extract. Considering energy consumption, US pasteurization is the most power consuming treatment despite its shorter duration. Overall, no univocal indication on the best pasteurization process can be gathered. Thus, it is necessary to define the desired target in order to drive technological interventions by a customized approach.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...