Digestion behavior and gastrointestinal fate of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by different modified rice starches
Abstract
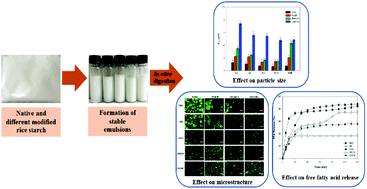
Native rice starch was modified using different methods which included debranching (DB), octenyl succinylation (OSA), debranching followed by octenyl succinylation (DBOS) and octenyl succinylation followed by debranching (OSDB). The effect of different modifications and the impact of modified starch properties (resistant starch content (RS) and degree of substitution (DS)) on the gastrointestinal fate of emulsified lipids are elucidated using an in vitro digestion model that included the mouth, stomach, and small intestine phases in order to understand their functionality for further applications. The effect of the different modified rice starches on the particle size distribution of the lipid droplets, surface charge (ζ-potential), microstructure, lipid digestion (free fatty acid (FFA) release), and starch hydrolysis was also assessed. The OSA-modified starch and DBOS starch-based emulsions were found stable during the mouth phase and were also found to demonstrate lesser flocculation and coalescence in comparison with the other emulsions due to the presence of more OSA groups that provide greater steric hindrance and better protection from the gastrointestinal conditions. Furthermore, the DBOS starch was found to form emulsions that were more resistant to digestion with a degree of FFA release like dietary fibers and a lower extent of starch digestion that can be attributed to their higher resistant starch content (RS). Thus, the DBOS starch-based emulsions were found to be suitable for further applications such as developing functional foods to control satiety or for designing delivery systems for the sustained release of bioactive compounds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...