Habitual animal fat consumption in shaping gut microbiota and microbial metabolites†
Abstract
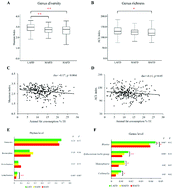
Short-term intervention studies support a link between animal-based diet and the outgrowth of microorganisms capable of triggering inflammatory bowel disease. However, whether habitual animal fat intake is associated with gut-related health remains unclear. Thus, we collected dietary information, clinical data and fecal samples from 297 healthy young subjects and characterized gut microbiota by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and microbial metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and bile acids (BAs) using a gas chromatography coupled to time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOF/MS) system and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) platform, respectively. We found that the microbial diversity of butyric acid (rho = −0.17, p = 0.004 for the Shannon index) and the concentrations of butyric acid (rho = −0.33, p < 0.001) and valeric acid (rho = −0.28, p = 0.002) were negatively associated with animal fat consumption. In line with this, the abundance of SCFAs-producing bacteria such as Blautia, Eubacterium hallii, and Megamonas were significantly lower in the high animal fat group compared with the low animal fat group (all p < 0.05). Additionally, the high animal fat group had higher concentrations of total (p = 0.06) and unconjugated (p = 0.09) BAs relative to the lower animal fat groups. The findings of our study indicate that a diet with higher animal-based fat consumption is likely to be associated with moderately unfavorable impacts on gut microbial diversity, community, and regulation of fecal SCFAs, which may influence the host cardiometabolic health in the long term among healthy Chinese adults whose diet is in a nutrition transition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...