Glycosaminoglycan from Apostichopus japonicus inhibits hepatic glucose production via activating Akt/FoxO1 and inhibiting PKA/CREB signaling pathways in insulin resistant hepatocytes
Abstract
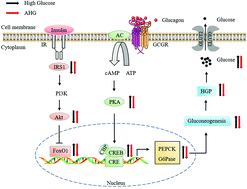
The aim of this study was to elucidate the effect and the underlying mechanism of glycosaminoglycan from Apostichopus japonicus (AHG) on hepatic glucose production (HGP) in insulin resistant hepatocytes. Insulin resistance was induced with high glucose (HG) for 24 h in primary hepatocytes. The results showed that AHG exhibited hypoglycemic activity at a relatively low concentration (1 μg mL−1) and revealed non-toxic activity to insulin resistant hepatocytes even at 500 μg mL−1 concentration. The HGP test showed that the treatment of AHG (10 μg mL−1) for 3 h decreased HGP by 25% in insulin resistant hepatocytes. Quantitative PCR and western blot analysis revealed that AHG also ameliorated phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase). The data revealed the mechanism of AHG in alleviating HGP via activating the Akt/FoxO1 signaling pathway and suppressing the PKA/CREB signaling pathway in insulin resistant hepatocytes. This finding suggests that AHG could be a potential marine natural product for the treatment of dysregulating glucose homeostasis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...