HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS screening of phytochemical compounds and the bioactive properties of different plant parts of Zizyphus lotus (L.) Desf.
Abstract
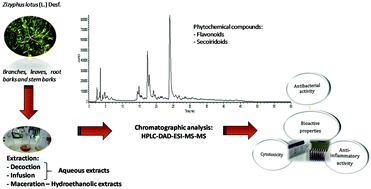
Zizyphus lotus L. (Desf.) has been widely used as a homemade ingredient to treat numerous diseases in Algerian folk medicine. In this context, decoction, infusion and hydroethanolic extracts were prepared from the branches, leaves, roots, and stem barks. The extracts were characterized regarding their phytochemical composition by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MSn and were assessed for in vitro bioactivity (cytotoxicity, anti-inflammatory activity, and antibacterial activity). A total of 29 compounds (flavonoid derivatives and secoiridoids) were identified in Z. lotus, 15 being detected in leaves, 10 in branches, 5 in roots and 7 in stem barks. The highest contents of these compounds, especially secoiridoids, were detected in branches followed by leaves, oleuropein being the main compound detected in leaves and oleoside in branches. The aqueous preparations of the leaves and root barks revealed the highest cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory potential. On the other hand, as for the antibacterial activity, the hydroethanolic extract of the branches showed the highest potential, especially against the MSSA strain. Hence, the chemical diversity found in Z. lotus makes it a source of bioactive ingredients that can be applied in the formulations of different ingredients in the food and pharmaceutical industries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...