Comparative study on foaming and emulsifying properties of different beta-lactoglobulin aggregates
Abstract
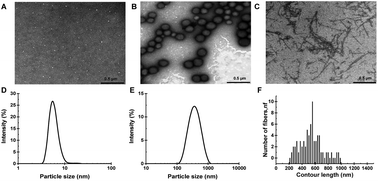
Different conditions in food processing lead to different aggregates of protein. β-Lactoglobulin nanoparticles (BLGNPs) and fibrils (BLGFs) were prepared by adjusting pH and temperature, and thereby their foaming and emulsifying properties were compared to native globular β-lactoglobulin (NGBLG) at pH 7.0 and pH 4.0. A foam analyser, a microparticle size analyser, an interfacial rheometer and an atomic force microscope (AFM) were used to characterise foaming/emulsifying functionalities and interfacial microstructures/mechanical properties. The foam and emulsion stabilities were assessed by measuring the decay of foam height and the variation of emulsion droplet size, and both were found to be in the order of BLGFs > NGBLG > BLGNPs. Foams were more stable at pH 4.0 while emulsions were more stable at pH 7.0. Surface dilatational modulus (E) of NGBLG and its aggregates at pH 4.0 was greater than that at pH 7.0, with BLGFs showing the highest value of E and thus the highest resistance to membrane damage. The emulsion prepared with NGBLG and its aggregates had more negative charges at pH 7.0 than at pH 4.0. The foaming stability seemed to be more controlled by interfacial elasticity while the emulsion stability was more determined by surface charges. AFM analysis demonstrated different microstructures at the air–water interface between pH 4.0 and 7.0 and among the different protein aggregates, which could well explain their foaming and emulsifying properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...