Encapsulation of ε-viniferin in onion-type multi-lamellar liposomes increases its solubility and its photo-stability and decreases its cytotoxicity on Caco-2 intestinal cells
Abstract
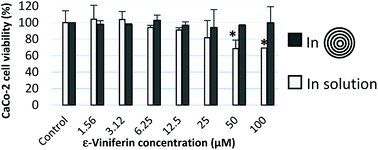
ε-Viniferin, a resveratrol dimer, is a naturally occurring stilbene that has been studied so far for its potential beneficial effects on human health. Its low water solubility, its photo-sensitivity and its low bioavailability make its applications in the food industry complicated. To overcome these limitations, ε-viniferin was encapsulated in phospholipid-based multi-lamellar liposomes (MLLs) called spherulites or onions. In the best case, an encapsulation efficiency of 58 ± 3% and a bioactive loading of 4.2 ± 0.5% were reached. Encapsulation of ε-viniferin drastically increased its water solubility by more than 5 orders to reach 17.4 g L−1 and provided protection against its UV-induced isomerization. While ε-viniferin was shown to be significantly toxic to Caco-2 intestinal-like cells for concentrations higher than 25 μM, once encapsulated in MLLs, those cells did not experience any mortality even for the highest tested stilbene concentration (100 μM) as revealed by red neutral assay.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...