Sclareol prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss in vivo and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro via suppressing NF-κB and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways†
Abstract
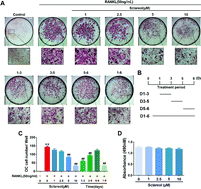
Postmenopausal osteoporosis (PMO) is a progressive disease occurring in elderly postmenopausal women that is characterized by low bone mass and impaired bone quality. Sclareol is a natural product (initially isolated from the leaves and flowers of Salvia Sclarea) that possesses immune-regulation and anti-inflammatory effects, but its role in osteoclastic formation and function as well as the PMO remains unknown. In the current study, we investigated the inhibitory effect of sclareol on osteoclastogenesis and progression of PMO. In vitro, sclareol not only inhibited osteoclast formation but also suppressed osteoclast function. The expression of the receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast marker gene and protein was also reduced by sclareol treatment. Mechanistically, we found that sclareol inhibits RANKL-induced NF-κB and MAPK/ERK pathway activation. Furthermore, sclareol exerted a protective effect against bone loss in an ovariectomy-induced mouse model. Taken together, our findings suggest that sclareol has potential value as a therapeutic agent for PMO.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...