Animal study of the anti-diarrhea effect and microbial diversity of dark tea produced by the Yao population of Guangxi†
Abstract
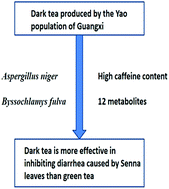
Chinese dark teas (CDTs) are a special type of tea traditionally consumed by ethnic minorities around the border regions of China. Dark tea produced by the Yao population of Guangxi could help prevent diarrhea following the heavy consumption of food. However, the underlying mechanisms behind this effect are not clear. This study aimed to investigate the function and underlying mechanisms of dark tea by examining the effects of different doses of dark tea on diarrhea in mice caused by Folium Sennae. It was found that dark tea could significantly improve the rate of loose stools and diarrhea index, and had an inhibitory effect on intestine peristalsis in high- and moderate-dose groups. Compared with green tea, significantly decreased levels of water extract, tea polyphenol and amino acid were found in dark tea, whereas the content of both caffeine and gallocatechin was increased. The result of dilution plating showed that Aspergillus niger and Byssochlamys fulva were consistent with microbial diversity as assessed by high-throughput sequencing technology. A total of 12 metabolites related to an anti-diarrhea effect were identified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). These findings provide a physiological basis for developing dark tea produced by the Yao population of Guangxi as a drink that can regulate and improve the intestinal flora in humans.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...