Establishing the impact of food matrix effects on the bioaccessibility of nutraceuticals and pesticides using a standardized food model
Abstract
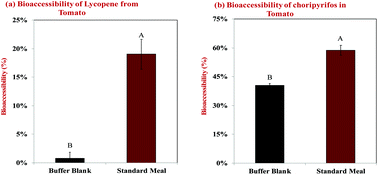
It is important to establish the impact of food matrix effects on the bioaccessibility of co-ingested substances, such as nutraceuticals, engineered nanomaterials, pharmaceuticals, and pesticides. Recently, a standardized food model (SFM) representing a typical US diet has been developed to facilitate these investigations. This model consists of caseinate-stabilized fat droplets, free casein, pectin, starch, sucrose, and sodium chloride. The SFM was stable to creaming for 2 days, contained small particles (d ≈ 180 nm), and had a narrow particle size distribution. The SFM was mixed with pureed tomato that had been deliberately contaminated with chlorpyrifos (a hydrophobic pesticide). The resulting mixture was then exposed to an in vitro digestion model. The structural and physicochemical characteristics of the samples (microstructure, particle diameter, and surface potential) were determined after each GIT stage. Also, the bioaccessibility of both chlorpyrifos and lycopene (a hydrophobic nutraceutical) from the pesticide-contaminated tomatoes was determined after the final digestion process. For lycopene, the bioaccessibility was much lower for tomato alone (0.75%) than for tomato plus SFM (19.0%) (p < 0.05). For chlorpyrifos, the bioaccessibility was also appreciably lower for tomato alone (40.4%) than for tomato plus SFM (58.7%), but the effect was less dramatic (p < 0.05). Our results indicate that a standardized food matrix impacts the bioaccessibility of hydrophobic bioactives in fresh produce by an amount that depends on the nature of the bioactive agent. The SFM developed here may therefore be useful for screening the potential impact of food matrix effects on the bioaccessibility of ingested bioactives and other substances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
