Bilberry anthocyanin extract promotes intestinal barrier function and inhibits digestive enzyme activity by regulating the gut microbiota in aging rats
Abstract
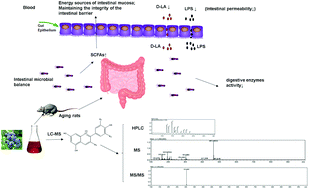
This study was aimed at understanding potential mechanisms regarding bilberry anthocyanin extract consumption and healthy aging and the effects on intestinal barrier function and digestive enzyme activity, through regulating the gut microbiota in aging rats. Medium-dose bilberry anthocyanin extract consumption (20 mg per kg bw per day) was the optimum amount to regulate the intestinal function of aging rats. After consumption, bacteria beneficial to the intestine (Aspergillus oryzae, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Clostridiaceae-1, the Bacteroidales-S24-7-group and the Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group) were induced to grow, and harmful bacteria (Verrucomicrobia and Euryarchaeota) were inhibited. However, high-dose bilberry anthocyanin extract consumption altered some intestinally beneficial bacteria in an adverse way. There was a correlation between changes in bacterial composition and changes in short-chain fatty acids and the intestinal mucosal barrier. Bilberry anthocyanin extract consumption also decreased the activity of digestive enzymes. Our results suggest that bilberry anthocyanin extract consumption is a potential approach for assisting healthy aging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...