Effect of dietary stevioside supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, serum parameters, and intestinal microflora in broilers
Abstract
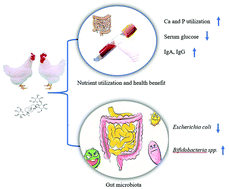
Disinhibition of antibiotics promotes the use of probiotics, prebiotics, immune enhancers, and plant extracts. We investigated the effects of stevioside on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, serum parameters, and intestinal microflora in broilers. Eight hundred ninety-six one-day-old male Arbor Acres broiler chicks (average body weight 48.36 ± 0.21 g) were allotted to 1 of 7 experimental treatments. Treatments consisted of: (1) control (basal diet without supplemental stevioside), (2) 100 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S100), (3) 200 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S200), (4) 400 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S400), (5) 800 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S800), (6) 1600 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S1600), and (7) 3200 mg kg−1 supplemental stevioside (S3200). Performance was not affected by stevioside concentration. Dietary stevioside supplementation increased the digestibility of calcium (P < 0.05) and tended to improve phosphorus digestibility (P = 0.0730). There was a linear effect of dietary stevioside on the concentration of serum glucose (P < 0.05). The serum IgG and IgA levels were linearly increased by stevioside supplementation (P < 0.05). In the ileal digesta, the concentration of E. coli decreased with increasing dietary stevioside supplementation (P < 0.05). On the contrary, dietary stevioside supplementation increased the concentration of Bifidobacteria (P < 0.01) and tended to improve the concentration of Lactobacillus (P = 0.0791). In conclusion, our data suggest that stevioside supplementation could improve the calcium and phosphorus digestibility and decrease blood glucose levels of broilers. Additionally, dietary stevioside supplementation significantly increased Bifidobacteria in the cecal digesta, and decreased E. coli.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...