Critical assessment of wet-chemical oxidation synthesis of silicon quantum dots†
Abstract
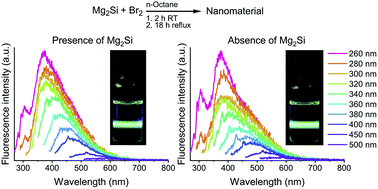
Wet-chemical synthetic procedures are powerful strategies to afford fluorescent silicon quantum dots (Si QDs) in a versatile and scalable manner. However, development of Si QDs is still hampered by a lack of control over photoluminescence emission, in addition to synthesis and characterization complexities. The wet-chemical Si QD synthesis by oxidation of magnesium silicide (Mg2Si) with bromine (Br2) was revisited and a control reaction was carried out where the silicon source was omitted. Both reaction conditions resulted in substantial quantities of fluorescent material. Moreover, a comparative analysis of their optical properties (UV-vis/fluorescence) revealed no apparent differences. Other characterization techniques also confirmed the resemblance of the two materials as 1H NMR, FTIR and XPS spectra were nearly identical for both samples. Elemental analysis revealed the presence of only 2 wt% silicon in the Si QD sample. No evidence was found for the formation of significant amounts of Si QDs via this wet-chemical procedure.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Luminescent silicon nanostructures


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...