Understanding electronic effects on carboxylate-assisted C–H activation at ruthenium: the importance of kinetic and thermodynamic control†
Abstract
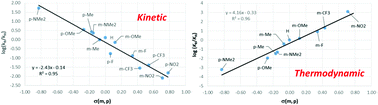
Meta- and para-substituted 1-phenylpyrazoles (R-phpyz-H) react with [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2 in the presence of NaOAc to form cyclometallated complexes [M(R-phpyz)Cl(p-cymene)] (where R = NMe2, OMe, Me, H, F, CF3 and NO2). Experimental and DFT studies indicate that product formation can be reversible or irreversible depending on the substituents and the reaction conditions. Competition experiments show that the kinetic selectivity favours electron-donating substituents and correlate well with the Hammett parameter, giving a negative slope (ρ = −2.4) that is consistent with a cationic transition state. However, surprisingly, the thermodynamic selectivity is completely opposite, with substrates featuring electron-withdrawing groups being favoured. These trends are reproduced with DFT calculations that locate a rate-limiting transition state dominated by Ru–O bond dissociation and minimal C–H bond elongation. Detailed computational analysis of these transition states shows that C–H activation proceeds by an AMLA/CMD mechanism through a synergic combination of a C–H→Ru agostic interaction and C–H⋯O H-bonding. NBO calculations also highlight a syndetic bonding term, and the relative weights of these three components vary in a complementary fashion depending on the nature of the substituent. With meta-substituted ligands H/D exchange experiments signal kinetically accessible ortho-C–H activation when R = NMe2, OMe and Me. This is also modelled computationally and the calculations highlight the kinetic relevance of the HOAc/Cl exchange that occurs post C–H bond cleavage, in particular with the bulkier NMe2 and Me substituents. Our study highlights that the experimental substituent effects are dependent on the reaction conditions and so using such studies to assign the mechanism of C–H activation in either stoichiometric or catalytic reactions may be misleading.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanistic processes in organometallic chemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...