Interfacial redox processes in memristive devices based on valence change and electrochemical metallization
Abstract
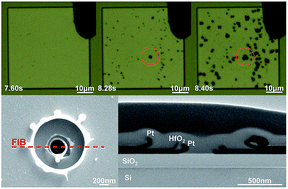
Memristive devices based on electrochemical processes are promising candidates for next-generation memory and neuromorphic applications. The redox processes happening at the interfaces are crucial steps for the ionization as well as generation of counter charges, and are thus indispensable for successful resistive switching, but their detailed mechanism has not been fully clarified. Here, we study the interfacial redox reactions in the forming process of memristive devices based on valence change and electrochemical metallization, using high-resolution electron microscopy and electrostatic force microscopy observations. We show direct evidence for the anodic oxidation of oxygen ions and cathodic reduction of moisture in HfO2- and Ta2O5-based valence change cells, which could take place in different horizontal locations. We further found that the anodic reactions always led to more pronounced structural damage to the electrode, indicating the possibility of additional cathodic reactions without producing gaseous products. When an active electrode is present, oxidation of metal atoms takes place at the anodic interface instead. Further investigations on electrochemical metallization cells have identified Cu ionization and moisture reduction as the anodic and cathodic reactions, respectively, and formation of Cu nuclei at the cathodic interface was directly observed. These findings with microscopic evidence could facilitate future development of memristive devices.
- This article is part of the themed collection: New memory paradigms: memristive phenomena and neuromorphic applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...