Removal of chloride ions using a bismuth electrode in capacitive deionization (CDI)
Abstract
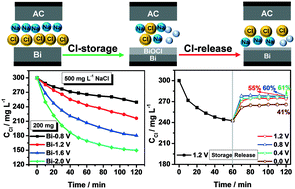
Non-carbon materials in capacitive deionization (CDI) can help to enhance the capacity of removed ions. Here, we report for the first time the removal of chloride ions (Cl−) with a bismuth (Bi) anode when coupled with an activated carbon (AC) cathode in CDI. The effects of carbon black in the Bi electrode, applied voltage, electrode mass loading and initial concentration on Cl− removal are investigated. Moreover, its cycle performance is also tested. Results show that addition of carbon black to a Bi electrode (Bi@CB) significantly improves Cl− removal. The declining trend of Cl− concentration and appearance of peaks assigned to products of bismuth oxychloride (BiOCl) in XRD patterns confirm Cl− storage by the Bi electrode, which is enhanced with an increase in voltage. When coupled with AC in a fixed mass, increasing the Bi mass does not contribute to more Cl− removal. Although the cycle performance is not excellent (the attenuation rate is 74% after 10 cycles), its chloride removal capacity is ∼2–3 times the value of AC (e.g. 0.95 vs. 0.32 mmol gBi−1 at 1.2 V in 500 mg L−1 NaCl solution). Besides, the Bi–AC electrode pair in CDI is more suitable to remove Cl− from a solution with a Cl− concentration of below 600 mg L−1.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Capacitive deionisation and electrosorption 2020

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...