Preventing the colloidal dispersion of Pb(iv) corrosion scales and lead release in drinking water distribution systems†
Abstract
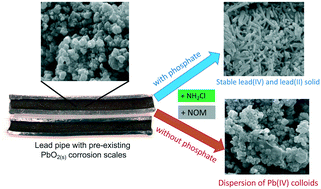
Lead(IV) oxide PbO2 is one dominant solid phase in lead corrosion scales of drinking water distribution systems. Understanding the colloidal dispersion of PbO2 is important for lead control in drinking water, especially under scenarios of switching the residual disinfectant from chlorine to chloramine. This study investigated the changes in lead release and colloidal dispersion from PbO2(s) associated with the presence of natural organic matter (NOM), the introduction of chloramine, and the addition of a phosphate corrosion inhibitor in drinking water distribution systems. Experimental data showed that when NOM was present, the surface charges of PbO2 exhibited a prominent negative shift, leading to colloidal dispersion of Pb(IV) particles. The presence of chloramine did not significantly change the detrimental effects of NOM on the colloidal behavior of PbO2. In contrast, the addition of phosphate greatly reduced colloidal lead release in the size range between 0.1 and 0.45 μm, and limited lead release with colloidal sizes less than 0.1 μm to below 15 μg L−1, i.e., the U.S. EPA regulatory standard. The beneficial effects of phosphate addition are mainly attributed to the suppression in colloidal dispersion of Pb(IV) particles. Meanwhile, the presence of phosphate also limits the reductive dissolution of PbO2via the formation of hydroxypyromorphite Pb5(PO4)3OH particles. Results from this study suggest that phosphate limits the dispersion of PbO2(s) by NOM and prevented the release of Pb(IV) colloids into drinking water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...