Status and challenges in photocatalytic nanotechnology for cleaning air polluted with volatile organic compounds: visible light utilization and catalyst deactivation
Abstract
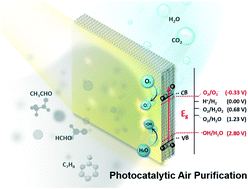
Photocatalysis that utilizes semiconductor nanoparticles is one of the most investigated environmental nanotechnologies. It is a promising technology for air purification because it can decompose gaseous pollutants (particularly volatile organic compounds (VOCs)) directly into harmless CO2 and H2O under ambient conditions. Photocatalysis can be particularly suitable for removing low concentration pollutants (sub-ppm levels) in indoor environments where conventional adsorption technologies are not very efficient. Although photocatalytic air purification has been extensively investigated, it still falls far short of satisfying the requirements for practical usage. This review focuses on two main critical issues for improving the applicability of photocatalytic air purification: (1) increasing visible light activity to utilize ambient light and (2) preventing catalyst deactivation that hinders long-term usage of photocatalysts. Literature reports on the photocatalytic degradation of VOCs using visible light are surveyed and systematically categorized based on the type of photocatalytic materials and VOCs. Strategies taken to significantly increase the efficiency of visible light photocatalysts are introduced. On the other hand, photocatalyst deactivation processes are discussed according to the kinds of air pollutants, and various methods of assessing the extent of photocatalyst deactivation are outlined. The development of deactivation-resistant photocatalysts and their applications to air purification are also introduced and discussed. Finally, the status and the problems of the current research on photocatalytic air purification are critically discussed and suggestions for future studies of photocatalytic air purification are made.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...