Zero-wastewater capacitive deionization: selective removal of heavy metal ions in tap water assisted by phosphate ions†
Abstract
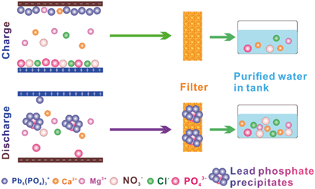
Removing trace toxic heavy metals such as Pb2+ completely from drinking water is important for protecting human health. However, healthy ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ in reasonable concentrations are beneficial to human health and thus do not need to be removed. Here we report a zero-wastewater capacitive deionization (CDI) technology using a thiol-functionalized graphene oxide/activated carbon (GO/AC) composite material for the selective removal of heavy metal ions in tap water. The thiol groups have a strong affinity to heavy metal ions (such as Pb2+), leading to very high Pb removal selectivity against Ca2+ and Mg2+. More importantly, native phosphate ions were found to significantly modify the CDI process in tap water. The presence of phosphate ions leads to the formation of Pb particulates with free ions in the tap water. During charging the particulates are removed by electrosorption onto cathodes while the accumulated Pb particulates are released upon discharging, forming precipitates by reacting with concentrated phosphate ions from anodes. The precipitates can be subsequently collected using filters equipped in the pipeline, thereby leading to a zero-wastewater CDI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
