Interaction of antibacterial silver nanoparticles and microbiota-dependent holobionts revealed by metatranscriptomic analysis†
Abstract
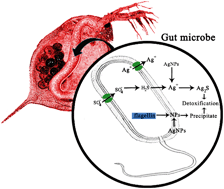
Although antibacterial silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are increasingly released into the environment and are very toxic to aquatic organisms, their effects on bacteria-based holobionts have been rarely studied. Here, we investigate the interactions between gut microbiota and zooplankton, Daphnia magna, under AgNP exposure through bioimaging, metatranscriptomic and gut microbiota translational techniques. The results demonstrated that the toxic symptoms of zooplankton were mediated by the gut microbiota at low concentrations of AgNPs, and the level of toxicity was influenced by the exposure time. At high AgNP concentrations, the mortality of zooplankton was due to the combined effects of the extinct gut microbiota and the accumulated toxicity. Exposure to AgNPs caused down-regulation of genes encoding proteasome, ATP synthesis, fatty acid biosynthesis, and β-oxidation in the host, with a shorter body length and decreased digestion and reproduction ability. These perturbations were relieved possibly through microbial sulfidation of Ag+, via the aggregation of nanoparticles and possibly the recovered synthesis of short-chain fatty acids (SFAs). The reduced fluorescence of AgNPs and the symptomatic palliation observed in the AgNP-tolerant microbiota inoculated D. magna further confirmed the detoxifying role of gut microbiota. Overall, our findings provide fundamental knowledge about the effects of AgNPs on bacteria-based holobionts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...