Oxidative stress and histological changes in Corbicula fluminea exposed to nano-Al13 and monomeric Al coagulants†
Abstract
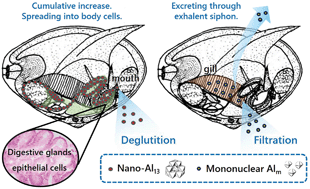
This is the first study to comprehensively analyze the toxicity of Al coagulants, which are widely present in the effluent of water treatment plants and in natural water in the form of polynuclear Al (e.g., nano-Al13) and mononuclear Al (Alm), on the siphoning efficiency, antioxidant defense system and histological alterations of Corbicula fluminea. The results showed that Alm had a stronger inhibitory effect on siphoning than the nano-Al13 coagulant. For all the selected enzyme indexes, induction by nano-Al13 was more intense in the digestive gland, while that by Alm was more obvious in the gills. Either Alm or nano-Al13 can enlarge the tubule lumen and reduce the thickness of the epithelia of digestive tubules, but nano-Al13 caused more severe damage to the cellular membrane. Inferred from the bright clusters observed by microscopy, granular nano-Al13 enters the digestive gland mainly via swallowing, while gill filtration is another method by which the ionic Alm can enter the clam body. The presence of nano-Al13 and inhibition of enzymes associated with GSH, such as GST and GR, led to the damage of cell membranes. For both Al coagulants, the influence of higher concentrations is more negative. As an effective coagulant, the toxicity of PACl cannot be ignored.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...