Highly porous Ce–W–TiO2 free-standing electrospun catalytic membranes for efficient de-NOxvia ammonia selective catalytic reduction
Abstract
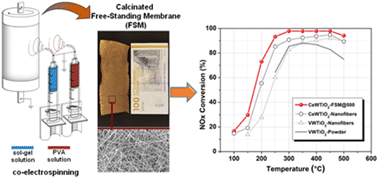
Highly porous Ce–W–TiO2 free-standing nanofibrous membranes (FSM) are fabricated via electrospinning techniques to serve as NOx-SCR catalysts. The precursor of the ceramic nanofibers (sol–gel solution) is co-electrospun with poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) water solution. PVA integration into FSM has been proven to avoid excessive bending of the nanofibers and to prevent mechanical failure of the final ceramic nanofibrous structure. This is demonstrated to be associated with higher thermal stability of PVA compared with that of other organic additives. 3D tomography reconstruction indicates a resulting ceramic membrane with remarkable open and interconnected porosity of ca. 96%. Catalytic characterization, performed at the best working conditions (in absence of H2O and SO2), indicates that amorphous FSM is the best performing catalytic membrane. Superior catalytic performances of the developed FSM over those of other nanofibers and nanoparticle catalysts are proven because of superior surface, morphological, and structural features. Long-term stability (120 h) and reproducibility (over 5 cycles) of FSM are also demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...