Recovery of gold from wastewater using nanoscale zero-valent iron†
Abstract
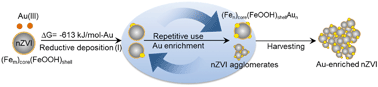
Herein we report a feasibility study on the enrichment and recovery of gold from industrial wastewater with nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI). In particular, a large-scale application (350 m3 d−1) using nZVI (150 kg d−1) to recover gold from hydrometallurgical smelting wastewater is presented. Over 5000 grams of gold was recovered from ∼120 000 m3 wastewater in a 12-month period. Trace gold in the wastewater (37 μg L−1) was recovered completely, with the harvested nZVI containing ∼41 g-Au per ton-nZVI on average. This work demonstrates important advantages of nZVI for the recovery of heavy metals from wastewater. The advantages can be attributed to the large driving force (ΔG = −613 kJ per mol-Au) of the nZVI-Au(III) reactions and the unique core–shell structure and surface chemistry of nZVI for heavy metal recovery. Batch experiments show the complete sequestration of Au(III) at a ppb level and over a wide concentration range (from 5.5 to 25 000 μg L−1) using a relatively low dose of nZVI (0.2–1.0 g L−1); the nZVI remained reactive over an extended period (>5 d); characterization of the reacted nZVI showed the formation and deposition of metallic gold nanoparticles on the nZVI, and the gold-carrying nZVI existed primarily as separable micron-sized aggregates (D50: 6.8–19.8 μm): in other words, nZVI, as a solid particle, also functions as a seed enabling the quick formation of separable products from a low gold source. This study illustrates tremendous potential of nanomaterials for resource recovery, and the strategies presented in this work may be equally applicable to the recovery of other elements in wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...