Mandelic acid and phenyllactic acid “Reaction Sets” for exploring the kinetics and mechanism of oxidations by hydrous manganese oxide (HMO)†
Abstract
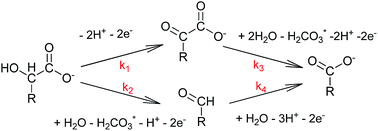
At pH 4.0, hydrous manganese oxide (HMO) oxidizes mandelic acid by two mole-equivalents of electrons, yielding phenylglyoxylic acid and benzaldehyde. These intermediates, in turn, are oxidized by two mole-equivalents of electrons to the same ultimate oxidation product, benzoic acid. The four compounds of the “reaction set” just described are conveniently monitored using capillary electrophoresis (CE) and HPLC. Extents of adsorption are negligible and their sum exhibits mass balance. Concentrations of phenylglyoxylic acid, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid can therefore be used to calculate mole-equivalents delivered to HMO for comparison with experimentally-determined dissolved MnII concentrations. Semi-log plots (ln[substrate] versus time) and numerical analysis can also be used to explore rates of oxidation of the functional groups represented, i.e. an α-hydroxycarboxylic acid, an α-ketocarboxylic acid, and an aldehyde. Inserting a –CH2– group between the benzene ring and the functional groups just described yields a new reaction set comprised of phenyllactic acid, phenylpyruvic acid, and phenylacetaldehyde, plus the C-1 ultimate oxidation product, phenylacetic acid. At pH 4, mass balance for phenyllactic acid oxidation fell short by ∼9%. Phenyllactic acid was oxidized 2.7-times more slowly than mandelic acid, while phenylpyruvic acid was oxidized 12.7-times faster than phenylglyoxylic acid. Unlike benzaldehyde, oxidation rates for phenylacetaldehyde were too fast to measure. Under pH 4.0 conditions, this reaction set approach was used to explore the acceleratory effects of increases in HMO loading and inhibitory effects of 500 μM phosphate and pyrophosphate additions. Mandelic acid and phenyllactic acid were oxidized by HMO far more slowly at pH 7.0 than at pH 4.0. At pH 7.0, 2 mM MOPS and phosphate buffers did not yield appreciable dissolved MnII, despite oxidation of organic substrate. 2 mM pyrophosphate, in contrast, solubilized HMO-bound MnII and MnIII.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...