Oxalate-enhanced solubility of lead (Pb) in the presence of phosphate: pH control on mineral precipitation
Abstract
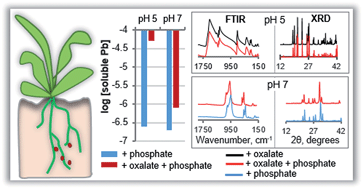
Here we study the precipitation of lead (Pb)-phosphate minerals over the pH range of 4.0 to 8.0 with and without oxalate, a ubiquitous and abundant low-molecular-weight organic acid derived from plants and microorganisms in environmental matrices. In the aqueous Pb-phosphate systems, phosphate precipitated Pb efficiently, reducing the dissolved Pb concentration below 1 μM at all the tested pH values, with the minimum solubility of about 0.1 μM measured at the intermediate pH of 6.0. The measured dissolved Pb and free Pb2+ ion activity were not in agreement with predictions from generally-accepted solubility products of the Pb phosphate minerals, particularly hydroxypyromorphite [Pb5(PO4)3OH]. Discrepancies between our measured Pb phosphate solubility products and older reported values are attributed to non-ideal behavior of these minerals (incongruent dissolution) as well as uncertainties in stability constants for soluble Pb-phosphate ion pairs. The presence of equimolar levels of oxalate and phosphate resulted in up to 250-fold increase in Pb solubility at acidic pH and about a 4-fold increase at pH 7.0, due to the strong suppression of Pb phosphate precipitation by oxalate and formation of soluble Pb-oxalate complexes. At pH 4.0 and 5.0, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) identified a Pb-oxalate mineral phase as the only precipitate despite the presence of phosphate; in the absence of oxalate, Pb hydrogen phosphate, PbHPO4, stably formed under these acidic conditions. At pH 6.0 and greater, FTIR and XRD data revealed that Pb-phosphate [Pb3(PO4)2], and hydroxypyromorphite [Pb5(PO4)3OH] to a lesser extent, were the predominant precipitates both in the absence and presence of oxalate. Therefore, oxalate did not strongly interfere with Pb-phosphate mineral formation at aqueous pH greater than 6.0 but oxalate controlled Pb solubility at acidic pH values.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...