Impact of bisphenol A influent concentration and reaction time on MnO2 transformation in a stirred flow reactor†
Abstract
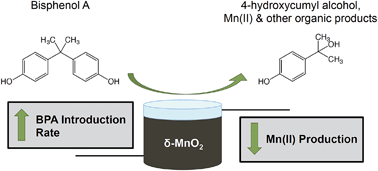
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an endocrine disrupting compound commonly found in natural waters at concentrations that are considered harmful for aquatic life. Manganese(III/IV) oxides are strong oxidants capable of oxidizing organic and inorganic contaminants, including BPA. Here we use δ-MnO2 in stirred flow reactors to determine if higher influent BPA concentrations, or introduction rates, lead to increased polymer production. A major BPA oxidation product, 4-hydroxycumyl alcohol (HCA), is formed through radical coupling, and was therefore used as a metric for polymer production in this study. The influent BPA concentration in stirred flow reactors did not affect HCA yield, suggesting that polymeric production is not strongly dependent on influent concentrations. However, changes in influent BPA concentration affected BPA oxidation rates and the rate of δ-MnO2 reduction. Lower aqueous Mn(II) production was observed in reactors at higher BPA introduction rates, suggesting that single-electron transfer and polymer production are favored under these conditions. However, an examination of Mn(II) sorption during these reactions indicated that the length of the reaction, rather than BPA introduction rate, caused enhanced aqueous Mn(II) production in reactors with low introduction rates and longer reaction times due to increased opportunity for disproportionation and comproportionation. This study demonstrates the importance of investigating both the organic and inorganic reactants in the aqueous and solid phases in this complex reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...