Semiconductor self-assembled monolayers as selective contacts for efficient PiN perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
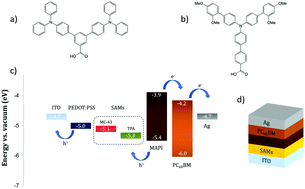
Herein, we studied the use of two different Self Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) made of semiconductor hole transport organic molecules to replace the most common p-type contact, PEDOT:PSS, in PiN methyl ammonium lead iodide perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The SAM molecule (MC-43) leads to a solar to energy conversion efficiency of 17.3, which is among the highest efficiencies reported to date for PiN perovskite solar cells. The present finding highlights the potential of semiconductor based SAMs to fabricate stable and high performing planar PSCs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...