Two zinc metal–organic framework isomers based on pyrazine tetracarboxylic acid and dipyridinylbenzene for adsorption and separation of CO2 and light hydrocarbons†
Abstract
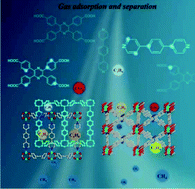
Two highly porous metal–organic framework isomers Zn2(TCPP)(DPB) (1 and 2, H4TCPP = 2,3,5,6-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)pyrazine and DPB = 1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)benzene) were successfully synthesized using different solvents and acid species to adjust the topologies of these two MOFs. Both of them were constructed by paddlewheel Zn2(COO)4, TCPP4−, and DPB ligands. In compound 1, the Zn2(COO)4 paddlewheel units were fitted together by the TCPP4− ligands to form two-dimensional layers, which were further connected by DPB ligands as pillars to construct a two-fold catenated 3D framework. In compound 2, the cross-linkage of Zn2(COO)4 paddlewheel units and TCPP4− ligands resulted in a three-dimensional framework of Zn-TCPP, in which DPB ligands coordinated to two axial vertical dinuclear Zn2(COO)4. Both activated MOFs exhibited permanent porosity with high BET areas (1324 m2 g−1 for 1 and 1247 m2 g−1 for 2) and possessed narrow pore size distributions (0.93 nm for 1 and 1.02 nm for 2). Moreover, the adsorption behaviors of the two activated MOFs for CO2 and light hydrocarbons (C1, C2, and C3) at low pressure were evaluated and favorable selectivity was proven for C3H8/C3H6 over CH4. These two MOF materials reported in this study for selective CO2 and light hydrocarbon capture have immense potential applications for environmental protection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...