The displacement reaction mechanism of the CuV2O6 nanowire cathode for rechargeable aqueous zinc ion batteries
Abstract
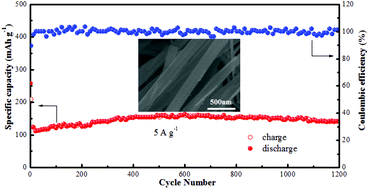
The development of high capacity, low cost, and high safety cathode materials for rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) is an ongoing challenge. Herein, CuV2O6 nanowires are prepared by a facile hydrothermal method to be used as a high-capacity cathode material for ZIBs. The sample displays an initial discharge capacity of 338 mA h g−1 at a current density of 100 mA g−1 and a capacity of 143 mA h g−1 remained at 5 A g−1 after 1200 cycles with a retention of ∼100% except for the initial capacity decay. Systematic structural and elemental characterization confirms that the reduction/oxidation of Cu2+/Cu0 is reversible during the electrochemical process. This work provides new prospects for designing more cathode materials based on the displacement reaction mechanism for Zn-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...