Hexaiododiplatinate(ii) as a useful supramolecular synthon for halogen bond involving crystal engineering†
Abstract
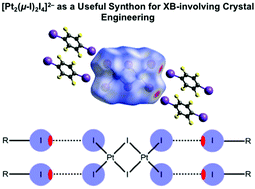
Hexaiododiplatinates(II) bearing ammonium and phosphonium cations, [R4N]2[Pt2(μ-I)2I4] {R = Et (1) and n-Bu (2)} and [R3PR1]2[Pt2(μ-I)2I4] {R = n-Bu and R1 = n-Bu (3); R = Ph and R1 = Ph (4); R = Ph and R1 = CH2Ph (5)}, were synthesized and characterized by high resolution ESI-MS, 1H, 13C{1H}, 31P{1H}, and 195Pt NMR spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray powder diffraction, and also electrostatic surface potential calculations. Complexes 1–3 were cocrystallized with halogen bond (XB) donors based on organic iodides featuring electron withdrawing groups {REWGIs: 1,3,5-triiodotrifluorobenzene (1,3,5-FIB), iodopentafluorobenzene (IPFB), 1,4-diiodotetrafluorobenzene (1,4-FIB), and tetraiodoethylene (C2I4)} to give crystalline adducts 1·2(1,3,5-FIB), 1·2IPFB, 2·2(1,4-FIB), and 3·C2I4. Inspection of the XRD data of the obtained adducts revealed the presence, in all four structures, of intermolecular REWGI⋯I–Pt XBs between the iodine centers of REWGIs and the terminal iodide ligands of [Pt2(μ-I)2I4]2− anions, where the latter act as rectangular XB-accepting synthons forming XBs with two, three, and even four Pt–Iterminal ligands. The results of Hirshfeld molecular surface analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations (the M06/DZP-DKH level of theory) followed by topological analysis of the electron density distribution within the framework of Bader's approach (QTAIM) confirmed the existence of the detected XBs, and their estimated energies vary from 2.2 to 4.7 kcal mol−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...