The impact of metal cations on the photochemical properties of hybrid heterostructures with infinite alkaline-earth metal oxide clusters†
Abstract
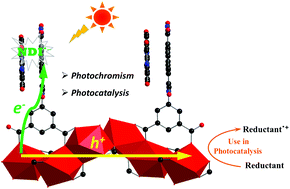
Donor–acceptor (D–A) hybrid heterostructures are an emerging class of hybrid complexes with potential applications in current optoelectronic technologies. To achieve high photoinduced charge-carrier generation and separation in a heterostructure, a common strategy is the fabrication of continuous or bicontinuous structures by the crystallization of semiconductive donor and acceptor tectons at the molecular level. So far, only a few such heterostructures have been fabricated, most of which involve unstable and narrow band gap metal halides. In this paper, we extended these unique hybrid heterostructures to continuous alkaline-earth metal oxide clusters. The combination of the naphthalene diimide (NDI) tecton bearing four carboxylates at two extremities with Ca2+ (or Sr2+) cations led to two isostructural D–A hybrid heterostructures with infinite 1-D carbon-doped alkaline-earth metal oxide clusters and X-aggregated NDI dimers as electron donors and acceptors, respectively. Due to the different metal cations in inorganic clusters, they exhibited diametrically opposite photochromic sensitivities and photocatalytic activities. To better rationalize them, a plausible photoinduced electron transfer process for the D–A hybrid heterostructures with photoactive acceptors has been developed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...